What is a Smart Factory?
The term “smart factory” often conjures images of futuristic, fully automated plants, but the reality is more nuanced. A smart factory isn’t just about robots; it’s about integrating various technologies to optimize every aspect of manufacturing, from design and production to supply chain and customer service. This integration typically involves technologies like IoT (Internet of Things) sensors, machine learning algorithms, big data analytics, and cloud computing, working together to enhance efficiency, productivity, and quality control.
The Pillars of a Smart Factory: Automation and Data
Automation is a cornerstone of the smart factory, but it’s not just about replacing human workers. Smart automation focuses on streamlining processes, making them more efficient and less prone to errors. This includes automating repetitive tasks, using robots for physically demanding jobs, and employing automated guided vehicles (AGVs) for material handling. Equally important is the role of data. Sensors embedded in machinery collect real-time data on performance, allowing for predictive maintenance, identifying potential problems before they cause downtime. This constant stream of data, analyzed through sophisticated algorithms, helps optimize production, reduce waste, and improve overall efficiency.
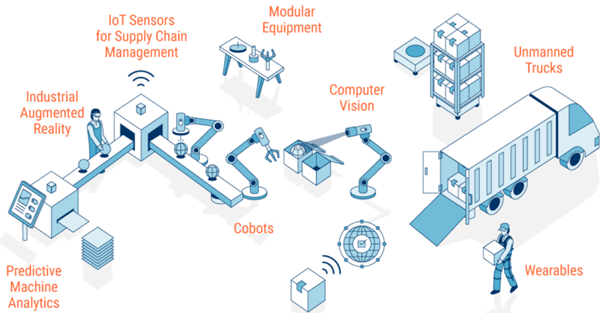
The Role of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are transforming smart factories by providing capabilities that go beyond simple automation. AI-powered systems can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and predict future outcomes. This allows for proactive adjustments in production schedules, optimized resource allocation, and improved quality control. Machine learning algorithms can constantly learn and improve, adapting to changing conditions and refining processes for maximum efficiency. For instance, ML can analyze sensor data to predict when a machine is likely to fail, allowing for preventative maintenance and avoiding costly downtime.
Enhanced Connectivity and the Internet of Things
The Internet of Things (IoT) is central to the functionality of a smart factory. Countless sensors, connected through a network, monitor every aspect of the production process, from the condition of machinery to the flow of materials. This interconnectedness enables real-time monitoring, data analysis, and rapid responses to changing conditions. The data collected by IoT devices informs decision-making at all levels, from adjusting individual machines to optimizing the entire production line. This improved connectivity also extends to the supply chain, allowing for better inventory management and more efficient logistics.
Improved Quality Control and Reduced Waste
Smart factories offer significant improvements in quality control and waste reduction. Real-time data monitoring allows for the immediate detection of defects and deviations from quality standards. This leads to faster identification and correction of problems, minimizing the production of faulty products. Furthermore, the analysis of production data helps identify areas where waste is generated, enabling optimization of processes and minimizing material usage. This translates to cost savings, reduced environmental impact, and a stronger commitment to sustainability.
The Human Element: Reskilling and Collaboration
While automation plays a crucial role in smart factories, humans remain vital. The shift towards smart manufacturing requires a workforce with new skills, capable of managing and interpreting data, operating sophisticated equipment, and collaborating with AI systems. Reskilling initiatives are essential to prepare the workforce for the demands of a smart factory environment. The focus shifts from performing repetitive tasks to higher-level roles involving analysis, problem-solving, and strategic decision-making. Human expertise in areas such as quality control, troubleshooting, and creative problem-solving remains indispensable, complementing the capabilities of automated systems.
Challenges and Considerations for Smart Factory Implementation
The transition to a smart factory presents significant challenges. The initial investment in technology and infrastructure can be substantial. Data security and privacy are critical concerns, requiring robust cybersecurity measures. Integrating various systems and ensuring seamless data flow can be complex. Effective change management is vital, addressing employee concerns and providing adequate training to ensure a smooth transition. Careful planning and a phased approach are essential for a successful implementation, allowing organizations to adapt and learn throughout the process.
The Future of Smart Factories: Continuous Improvement and Innovation
Smart factories are not static entities; they are continuously evolving systems. Advances in AI, machine learning, and other technologies will further enhance their capabilities. Future smart factories will likely feature even greater levels of automation, more sophisticated data analytics, and more seamless integration with supply chains and customers. The focus will remain on optimizing efficiency, improving quality, and responding quickly to changing market demands. The journey towards a truly smart factory is an ongoing process of innovation and improvement, constantly adapting to new technologies and evolving business needs. Read more about industry 4.0 in manufacturing.
