What is a Smart Factory?
The term “smart factory” conjures images of futuristic, automated production lines. While that’s partly true, it’s more accurately defined as a manufacturing environment that leverages advanced technologies to optimize processes, enhance efficiency, and improve overall productivity. This isn’t just about robots; it encompasses a holistic approach integrating data analytics, machine learning, the Internet of Things (IoT), cloud computing, and advanced automation to create a truly connected and responsive manufacturing ecosystem.
The Role of Data Analytics in Smart Factories
Data is the lifeblood of a smart factory. Sensors embedded in machines collect vast amounts of information on everything from production speeds and energy consumption to equipment performance and potential failures. Sophisticated data analytics tools then process this information, identifying trends, predicting issues, and providing real-time insights that enable proactive adjustments to optimize processes. This predictive maintenance, for example, helps prevent costly downtime by identifying potential equipment failures before they occur.
The Power of the Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things plays a critical role in connecting all the elements within a smart factory. From machines and sensors to robots and even individual components, IoT enables seamless communication and data sharing across the entire production line. This interconnectedness allows for real-time monitoring, automated responses to changing conditions, and improved overall visibility into the production process. Imagine a system that automatically adjusts production based on real-time demand fluctuations—that’s the power of IoT in a smart factory.
Automation and Robotics: The Driving Force of Efficiency
While not entirely new, automation and robotics are amplified within the smart factory context. Robots aren’t just performing repetitive tasks; they’re integrated into a larger system, collaborating with human workers and responding to dynamic conditions. Advanced robotics, often guided by AI, can handle complex tasks, improve precision, and enhance safety. This increased automation doesn’t necessarily mean fewer human jobs; rather, it allows human workers to focus on more strategic and creative roles, freeing them from repetitive or dangerous tasks.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) – The Brains of the Operation
AI and ML are the brains behind many smart factory operations. These technologies analyze the massive datasets generated by the IoT devices and other sources, enabling predictive maintenance, optimized resource allocation, and improved quality control. AI-powered systems can identify patterns and anomalies that might be missed by human operators, leading to faster problem-solving and more efficient production. Furthermore, machine learning algorithms continuously learn and improve, adapting to changing conditions and optimizing performance over time.
Cloud Computing: Enabling Scalability and Collaboration
Cloud computing provides the infrastructure necessary to support the vast amounts of data generated and processed within a smart factory. The cloud offers scalability, allowing manufacturers to easily adapt to changing demands and production volumes. Furthermore, cloud-based platforms facilitate collaboration between different departments, suppliers, and even customers, creating a more integrated and efficient supply chain. Data accessibility and storage are significantly enhanced, fostering better decision-making across the entire organization.
The Human Element: Collaboration, Not Replacement
It’s crucial to emphasize that smart factories aren’t about replacing human workers with machines. Instead, they’re about enhancing human capabilities and creating a collaborative environment where humans and machines work together. Human expertise remains essential for problem-solving, innovation, and strategic decision-making. The role of human workers shifts towards more sophisticated tasks such as overseeing complex processes, managing advanced technologies, and focusing on continuous improvement.
Challenges and Considerations for Smart Factory Implementation
Implementing a smart factory is a significant undertaking. The initial investment can be substantial, requiring careful planning and resource allocation. Furthermore, integrating different technologies and systems can be complex, requiring expertise in various areas. Data security and privacy are also significant concerns, requiring robust security measures to protect sensitive information. Finally, effective training and upskilling of the workforce are crucial to ensure successful adoption and maximize the benefits of a smart factory environment.
The Future of Manufacturing: A Smarter, More Efficient Industry
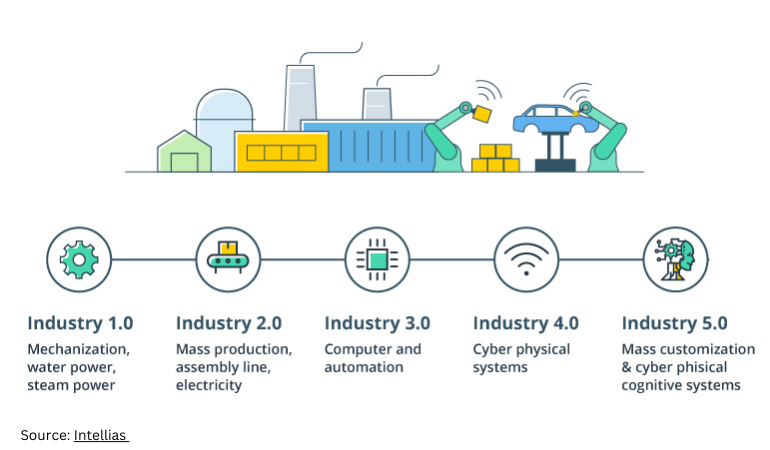
Smart factories are transforming the manufacturing landscape, driving efficiency, improving product quality, and increasing responsiveness to market demands. As technologies continue to evolve, smart factories will become even more sophisticated, interconnected, and adaptable. The future of manufacturing is undoubtedly smarter, more efficient, and more sustainable, thanks to the ongoing advancements in smart factory technologies. Click here to learn about the digital transformation of Industry 4.0.
